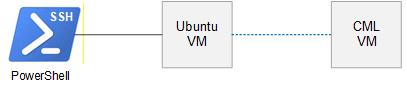
This article explains how to create a network automation lab from free software. It is essential that network engineers learn how to build, test, and debug automation scripts with AI tools.
Ubuntu Server VM is a control node with automation software installed that connects to Cisco Modeling Labs (Free). Ansible playbooks and Python scripts are included that can be run and modified for AI scripting practice. You will also learn how network as code (YAML) is used to import Cisco labs and how to create code with AI tools.
Table of Contents
- Disable Microsoft Hyper-V
- Install VMware Workstation
- Create Ubuntu Server VM
- Install Ubuntu Server Control Node
- Install Automation Software and Scripts
- Install Cisco Modeling Labs (Free)
- Import CML Automation Lab Topology
- Windows PowerShell SSH Connection
- AI-Powered Scripting Techniques
Disable Microsoft Hyper-V
VMware Workstation and Microsoft Hyper-V are not compatible on Windows Home Edition or Windows Pro. You will get a nested virtualization not supported error when starting CML with VMware. Nested virtualization feature enables Cisco IOS devices to run as separate VMs within Cisco CML VM.
Hyper-V is a Type 1 hypervisor that exclusively manages all hardware virtualization and prevents CML from using nested virtualization with VMware. The same problem will occur when using GNS3 and EVE-NG with VMware. This automation lab setup was tested with VMware Workstation 17.5 installed on Windows 11 Home and Windows 11 Pro. There are separate instructions included for both operating systems.
Disable Hyper-V (Windows Home Edition)
There is only partial support for Hyper-V included with Windows Home Edition. This makes it easier to disable Hyper-V and allow nested virtualization required with CML.
Start Windows PowerShell as Administrator and type the following command to disable Hyper-V launch from Windows. Hint: If you don’t know how to start Windows PowerShell as Administrator ask ChatGPT.
bcdedit /set hypervisorlaunchtype off
Uncheck the following features to disable Hyper-V components in Control Panel and then restart your computer:
Control Panel -> Select Programs -> Select Turn Windows Features on or off
1. Uncheck Virtual Machine Platform
2. Uncheck Windows Hypervisor Platform
3. Uncheck Windows Subsystem For Linux
Memory Integrity Setting:
Type core isolation in Windows search bar, select core isolation, and turn Memory Integrity setting OFF. You will have to restart your computer then continue with lab setup.
Disable Hyper-V (Windows Pro)
This article explains how to fully disable Hyper-V on a machine with Windows Pro. Hyper-V is fully supported with Windows Pro and this makes it more complex to disable all Hyper-V components. ChatGPT can provide instructions on how to reinstall Hyper-V software at a later date when VMware is uninstalled.
Install VMware Workstation
Start with VMware Workstation install using the default settings. Skip this step if VMware Workstation 17+ is already installed and proceed to Ubuntu Server install.
- Go to support.broadcom.com and log in (or register a free account with valid email)
- In the top-right corner, select “Support Portal”, then:
- Choose the VMware Cloud Foundation division.
- Click My Downloads.
- Search for “Workstation Pro”.
- Click on the product and choose the “Personal Use” (same binaries).
- Be sure to check the “I agree to the Terms and Conditions” box – it unlocks the download
- Choose the latest version (e.g., Workstation Pro 17.5.2+ or newer).
- Download and install VMware
- DO NOT install Windows Hypervisor Platform (WHP) option (leave it unchecked).
- On launch, select “Personal Use” if prompted — no license key needed.
Create Ubuntu Server Virtual Machine
Do NOT use an existing Ubuntu Server VM since this lab setup is configured to work with CML. Create a clean install based mostly on default settings except OpenSSH server install.- Download the ISO: Ubuntu Server 24.04 LTS from the official site
- Start VMware Workstation
- Select Create a New Virtual Machine
- Select Typical (recommended)
- Installer disc image file (iso)
- Browse to your downloads folder and select the Ubuntu Server 24.04 ISO
- Name the VM: Ubuntu-Lab
- Select a location to store VM files
-
Disk Settings:
– Minimum: 20 GB (default)
– Choose: Store virtual disk as a single file
Customize Hardware: (accept default settings) - Select Finish
– Memory: 2048 MB (minimum)
– Processors: 2 cores
– Network Adapter: NAT (default)
– CD/DVD: Should already point to the Ubuntu ISO
– Optional: Advanced → Firmware type, enable UEFI if not already selected
Install Ubuntu Server
Ubuntu terminal does not enable full screen view by default. You will have to scroll when navigating during install if display is low resolution or select Full Screen menu option.- Select language → Enter
- Select keyboard layout → Done
- Select type of installation (default) → Done
- Network configuration (default) → Done
- Skip proxy configuration (optional) → Done
- Mirror location test (wait until reading package lists appear) → Done
- Guided storage configuration (default use entire disk) → down arrow → Continue
- File system summary (default) → Done
- Select Continue to start installation
- Profile Configuration
- Your name:
- Server name:
- Username:
- Password:
- Skip Ubuntu Pro install option → Continue
- Install OpenSSH server → spacebar to select → down arrow → Continue
- Skip Featured Server Snaps → down arrow → Continue
- Installing system…
- When installation finishes, then Enter to reboot now
- Press Enter when ‘failed unmounting cdrom:unmount error’ occurs.
VMware DHCP configuration settings
The most current version of VMware (17.5) will often assign 192.168.216.0/24 subnet by default to NAT network (VMnet8). This is used for internet access, Ubuntu host VMs, and communication hub between VMs.
Verify / Update VMware DHCP
Cisco CML automation lab has a default gateway router (R1) with IP address 192.168.216.200/24 on interface E0/1 that links to external-connector. Ubuntu host VM must be assigned to the same subnet (192.168.216.0/24) to enable connectivity. The first step is to verify that VMware is using 192.168.216.0/24 subnet and if not then modify accordingly or select cancel. This update will typically have no effect on any existing VMs since DHCP will change IP addressing seamlessly.
- Select VMware Edit Menu
- Select Virtual Network Editor
- Change settings (administrator)
- Select VMnet8
- Subnet IP: 192.168.216.0 Subnet mask: 255.255.255.0
- Modify and restart VM or cancel if 192.168.216.0/24 already configured
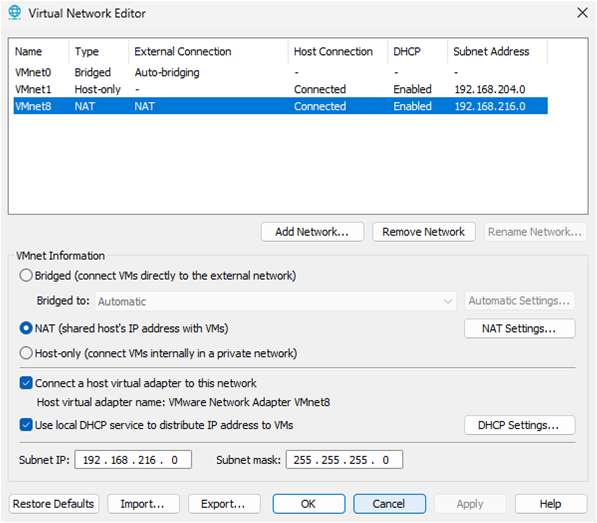
VMware external connections via NAT (VMnet8)
Install automation software
To prepare the Ubuntu control node for automation tasks you will download a bash script to your home directory. The bash script installs Python, Ansible, Netmiko, and a virtualized (venv) environment for automation. There is also configuration of static routes, rsyslog, and ansible.cfg for playbooks. The purpose of venv is to isolate your lab setup from Python global environment. This is a best practice so that all software and version updates apply only to your automation lab to prevent conflicts. Use clear command to declutter Ubuntu terminal of text.
Step 1: Login with the Ubuntu sudo username and password you created for this VM.Step 2: Download the bash script to your home directory:
username@ubuntu:~$ curl -O https://cisconetsolutions.com/ubuntu-automation-setup.shusername@ubuntu:~$ sudo chmod +x ubuntu-automation-setup.shusername@ubuntu:~$sudo ./ubuntu-automation-setup.shusername@ubuntu:~$ source ~/.bashrcYour network automation environment is now fully installed and configured. You’re ready to start building and testing automation scripts using nano editor and ChatGPT. The bash script added two static routes on Ubuntu control node for CML connection that can be displayed with ip route show command.
Install Cisco Modeling Labs (CML-Free)
Cisco Modeling Labs includes a free tier version with 5-node limit. Learn how to create and test automation scripts on real Cisco IOS. The is preferrable to emulated lab environments such as GNS3 and EVE-NG that are error prone and more complex to setup similar labs. You can also upgrade to CML Personal and use it for real lab testing at work and certification study. Share labs with a YAML text file instead of large binary project files used by GNS3 and EVE-NG.
- Create and test automation scripts on Cisco approved IOS.
- Less complex to setup than GNS3 or EVE-NG that are error prone.
- Share labs with a YAML text file instead of large binary projects.
- Upgrade to CML Personal for additional nodes.
This section explains how to install Cisco Modeling Labs (v2.8) to VMware Workstation and import a lab-ready (Network as Code) topology.
Download Cisco CML files
Step 1: You will need to first register for a Cisco CCO account. Skip this step if you already have an existing account.
Step 2: Navigate to the CML-Free Sign-up page to register for access to CML-Free.
https://mkto.cisco.com/cml-free.html
Step 3: Navigate to Cisco Software Download and login with your Cisco CCO account.
https://software.cisco.com/download/home
Step 4: Select Modeling Labs on right side-bar and then select CML-Free 2.8 release. The following CML files are for VMware and have been tested with CML 2.8 stable version.
Download CML 2.8.0 server software = cml2_2.8.0-6_amd64-32.ova
Download CML IOS reference platform (images) = refplat-20241016-fcs-iso.zip
Configure CML virtual machine
Step 5: Navigate to your Windows download directory. Close any existing VPN connection.
Step 6: Extract refplat-20241016-freetier-iso.zip to a folder for install.
Step 7: Right-click on cml2_f_2.8.1-14_amd64-35.ova and select Open with VMware Workstation.
Step 8: Follow prompts in the VMware Import Wizard.
Select VMware for personal use
Name for new virtual machine: CML
Storage path: default and select Import
Step 9: CML Virtual Machine settings will open (Do NOT start VM).
Step 10: Verify the following options are set accordingly.
Number of processors = 4
Number of cores per processor = 1
Check Virtualize Intel VT-x/EPT or AMD-V/RVI
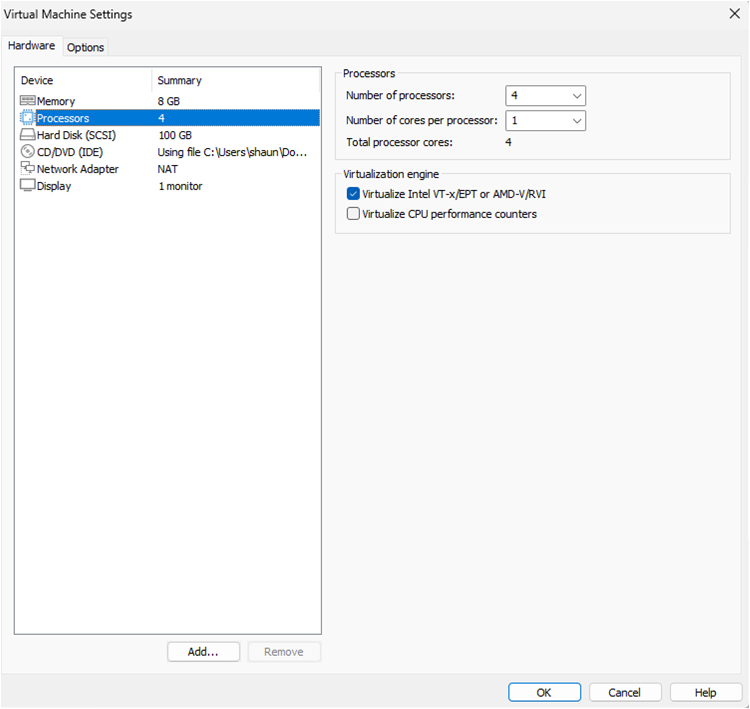
Memory: 8GB or more (recommended)
Hard Disk: Expand disk capacity to 100 GB minimum recommended and ignore message. The disk size will automatically resize when virtual machine is started. This is a maximum size only with thin provisioning that assigns disk space based on usage.
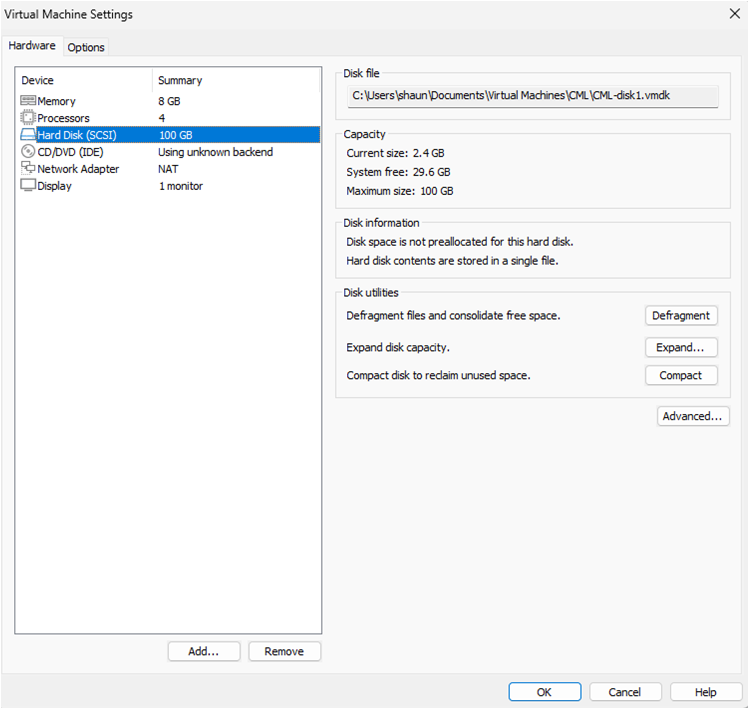
CD/DVD: Check the ‘use ISO image file’ check box. Browse to your downloads directory and open refplat-20241016-freetier-iso folder. Select refplat-20241016-freetier file.
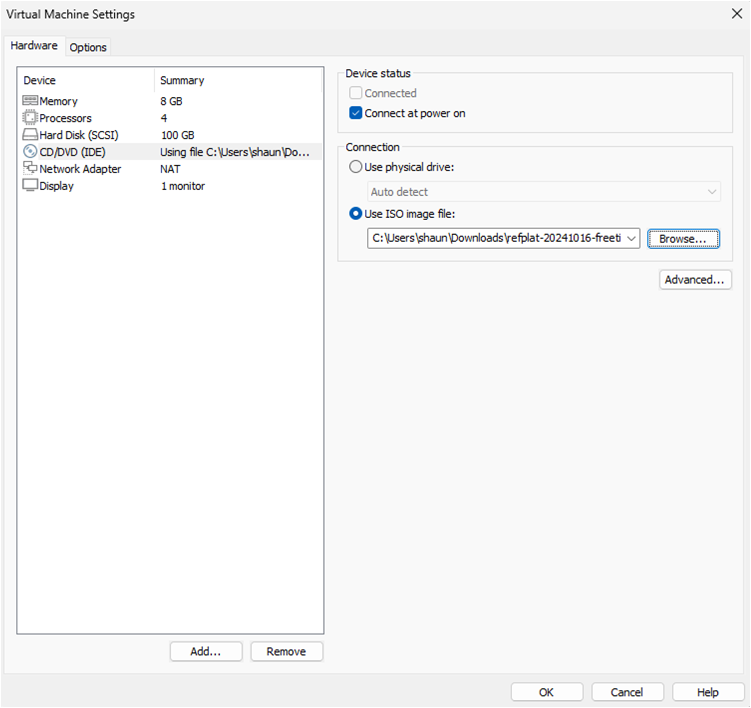
Check the ‘Connect at power on‘ check box.
Network Adapter: Select NAT
Step 11: Power on virtual machine and accept EULA (use arrow and tab keys).
CML application setup
Step 12: Confirm standalone all-in-one deployment.
Step 13: Enter system unique hostname: cml-controller (default)
Step 14: Create sysadmin account and assign password. Select yes to ignore password warnings.
Step 15: Create user admin account and assign password to access CML labs via Web UI. Select yes to ignore password warnings.
Step 16: Select continue for DHCP (default) to configure IPv4 addressing from VMware. This setting only applies to external connections such as the internet or inter-VM links.
Step 17: Confirm settings. CML will start copying refplat images at this point for Cisco devices. This could take several minutes to copy images based on your laptop speed. Select Continue button and wait for CML server to reset.
*Cisco CML official online documentation
Download automation lab (network as code)
Step 18: Click on link to download automation lab topology for import to CML. This is a text file approximately 30KB size that provides configured devices as shown. There are also some networking features that will be configured with Ansible and Python.

Step 19: Access CML UI from your browser with DHCP assigned IP address shown in the CML VM console (ignore 9090). Select Advanced button to ignore any SSL certificate warnings, and select Proceed.
This command is an example with CML default username admin and password you created when installing CML. The assigned IP address is only an example and could be different.
https://192.168.216.129
Username: admin
Password: **********
Step 20: Select Import and browse to your downloads directory. Select automation ready lab topology student_automation_lab.yaml and import into CML. Your browser could randomly disconnect from CML server when there is inactivity. Click your browser reload button to refresh web page only if this occurs.
Step 21: Select Start Lab and wait a minute for lab topology to initialize. This only occurs once when importing a new Cisco lab and sometimes will require starting an individual network device/s with right-click start lab option.
Step 22: Console and create SSH key on each Cisco device since they are not imported automatically. Press enter key to accept default 2048 bits key length.
device>enable
Password: cisco
device(config)#crypto key generate rsa
Choose the size of the key modulus. How many bits in the modulus (2048): Enter
Save the running configuration to startup configuration on each device.
device#copy run start
Windows PowerShell SSH access
The preferred method to access Ubuntu control node is from Windows PowerShell via SSH. This is recommended since PowerShell has Windows style terminal navigation, text readability, and easy to copy/paste text blocks. Creating your own scripts will require copy and paste from ChatGPT to Ubuntu nano editor. There is also copy and paste of script errors from Ubuntu to ChatGPT for troubleshooting or refactoring. Attempting to do this from within Ubuntu basic terminal is an exercise in frustration to say the least.
Step 1: Start with identifying the IP address that VMware has assigned to Ethernet interface (ens33) on Ubuntu control node:(cml-automation-venv) username@ubuntu:~$ ip aPS C:\Users\>ssh username@ip addressPS C:\Users\>username@ip address password: ********The following directory structure is automatically created when scripts.tar was untarred with bash script. Ansible playbooks are coded with vault feature for SSH password encryption and Python scripts use getpass feature for the same purpose.
*Do not test and/or debug any lab scripts included here in your production environment.
~/scripts/ansible
├── hosts.ini
├── vault.yaml
├── ping_check.yaml
├── ssh_connect_test.yaml
├── cisco_backups.yaml
├── vlan_config.yaml
├── etherchannel.yaml
├── loopback_interface.yaml
├── syslog.yaml
├── extended_acl.yaml
├── enable_secret_compliance.yaml
├── switch_status_check.yaml
├── post_deployment_check.yaml
├── /reports
├── /cisco_backups
~/scripts/python
├── devices.txt
├── switches.txt
├── ping_check.py
├── ssh_connect_test.py
├── interface_status.py
├── cisco_firmware_scan.py
├── encryption_compliance.py
├── switch_post_deployment_check.py
├── /reports
How to run Ansible playbooks
The following commands are used to run Ansible playbooks from Ubuntu control node. Ansible hosts.ini file is mandatory since it provides hostname and IP address of Cisco devices. The only Ansible playbook that does not use vault password is ping_check.yaml since there is no SSH login. Run Ansible playbooks from home/scripts/ansible directory and include –ask-vault-pass keyword for vault password. All text reports are saved to reports directory except cisco_backups and viewed with cat |more command. Start with SSH from PowerShell to Ubuntu based on your Linux username and IP address that VMware assigned to your VM. (e.g., 192.168.216.128)
ssh username@ip address
(cml-automation-venv) username@ubuntu:~$ clear
(cml-automation-venv) username@ubuntu:~$ ls -l
(cml-automation-venv) username@ubuntu:~$ cd scripts/ansible
(cml-automation-venv) username@ubuntu:~$ ansible-playbook -i hosts.ini ping_check.yaml
(cml-automation-venv) username@ubuntu:~$ ansible-playbook -i hosts.ini ssh_connect_test.yaml —ask-vault-pass
Vault password: cisco
How to run Python scripts
The following commands are used to run Python scripts from Ubuntu control node. You will be prompted for SSH username and password used for Cisco device login. There are devices.txt and switches.txt host files with hostname and IP address used by scripts. Run Python scripts from home/scripts/python directory. All .txt/.html reports are saved to reports directory and viewed with cat |more command.
(cml-automation-venv) username@ubuntu:~$ cd scripts/python
(cml-automation-venv) shaun@ubuntu:~$ python3 cisco_firmware_scan.py
SSH username: admin
SSH password: automation
Ansible playbook practice labs
The following are some suggestions for creating playbooks to modify the CML lab topology. They are all functional requirements that can be used as part of a ChatGPT prompt along with context to generate different playbooks. I have noted the inventory group names specified in hosts.ini that can be viewed with cat |more command. Follow the prompt engineering steps so that ChatGPT can generate accurate error-free scripts.
- configure switchport trunk allowed vlan 9-10,100 (L3_switches:L2_switches)
- enable service password-encryption on all devices (all_cisco)
- backup cisco configuration locally and push to Git repo (all_cisco)
- advertise loopback1 (172.16.255.0/32) via OSPF (routers:L3_switches)
- update Cisco firmware on routers based on recommendations (routers)
- configure default port security on access ports (L2_switches)
- configure PortFast and BPDU Guard on access ports (L2_switches)
- configure username noc privilege 1 secret noc-account for read access (all_cisco)
Python script practice labs
The following are some suggestions for creating Python scripts with ChatGPT to modify the CML lab topology. I have noted the hosts filename that should be pasted to ChatGPT prompt along with context and any other functional requirements for each prompt. Follow the prompt engineering steps so that ChatGPT can generate accurate error-free scripts.
- show interface status on switches (switches.txt)
- report down interfaces only (devices.txt)
- collect device hostname, model, serial number, ios software version (devices.txt)
- configure exec-timeout 1 to line vty 0 4 (devices.txt)
- detect interface collisions from duplex mismatch (switches.txt)
- parse running configuration: list ACLs and static routes on devices (devices.txt)
- configure minimum password-length 12 to all Cisco device passwords (devices.txt)
ChatGPT prompt engineering tips and tricks
You are ready to start using the automation lab and run scripts for testing and updates. The purpose of this automation lab is to learn how to create, run, and troubleshoot scripts with ChatGPT. All of the Ansible playbooks and Python scripts provided were 100% created with ChatGPT. Learn how to develop and test network automation scripts with ChatGPT. You can generate and troubleshoot scripts in seconds that would take you hours or days if at all.
Creating Ansible playbooks and Python scripts
Creating automation scripts with ChatGPT is an iterative process of prompt, test, debug, and validate. You will have ChatGPT debug errors along with how scripts are run and reports. This is common and results from prompts with missing details or context.
Prompt Engineering: The responses from ChatGPT are only as good as the prompts you input. Each prompt should provide context that includes your current setup and what you want to accomplish. This should include virtualization software, automation tools, hosts file, and Cisco network details for example. Then include functional requirements to define an effective prompt that ChatGPT can use to create script.
Context Example: VMware, Ubuntu Server control node 24.04, ansible vault enabled, SSH connect to Cisco devices, IOS-XE, IP addressing, paste hosts.ini file or python hosts file.
Functional Requirements Example: ansible playbook, backup startup configuration, explain purpose of script or paste IOS command/s, report format (.txt/html) and directory, security issues, addressing, cisco module features, verify updates, and save configuration.
Step 1: ChatGPT Prompt
My current setup is VMware with Ubuntu server control node that connects via SSH to Cisco devices running IOS-XE. Ansible vault.yaml is already configured with encrypted SSH password and enable secret password. This is my hosts.ini file for reference. Create an Ansible playbook based on this pasted hosts.ini file. The script should backup startup configuration first and then configure service password encryption on all devices from all_cisco inventory group. Print the results to terminal and also a text report saved to ~/scripts/ansible/reports directory. Save the running configuration and use Cisco module that supports idempotency, error checking, and configuration validation.
Step 2: Copy/Paste Script to Nano Editor
Start Ubuntu nano editor with the name of your new Ansible playbook or Python script. Paste the code copied from ChatGPT grey box to nano editor with right-click. Save the file with Ctrl-O and hit Enter to confirm write. Exit nano editor with Ctrl-X and return to Ubuntu command line.
(cml-automation-venv) username@ubuntu:~$ nano playbook.yaml
Step 3: Run Script
Create an automation lab where preliminary testing and debugging of scripts can be done without affecting the production network. It is recommended to have hosts file in the local working directory.
Step 4: Debug Script
Any error messages can be copied to ChatGPT for analysis and to modify script. There are often issues with how script runs and reports that do not necessarily generate error messages. Ask ChatGPT for a full modified playbook or script since mistakes are often made with pasting snippets into original script.
Step 5: Post-Run Validation Test Plan
Some examples of functional tests include HSRP failover, interface shutdown for routing behavior, or performance tests. You could verify Syslog operation for example by shutting down an interface and run cat /var/log/syslog command. This Ubuntu command will list the interface down system message generated at bottom of log. ACL tests are another example that involves sending destination traffic and verify filtering is working correctly.
ChatGPT Prompt: Python
My current setup is VMware with Ubuntu Server 24.04 control node that connect via SSH to Cisco L2 and L3 switches running IOS-XE. This is hosts file called switches.txt pasted here that lists IP addresses of switches. Python script must be implemented with getpass to prompt for SSH password and secret enable password. This is a security policy so that no device passwords are hard-coded in script. The script should backup startup configuration first and then parse running configuration to check if enable secret command is present on all target devices. Print the results to terminal and also a text compliance report saved to ~/scripts/python/reports directory.